Handling Multiple Wallets
The React Native SDK supports an arbitrary number of wallets at one time.
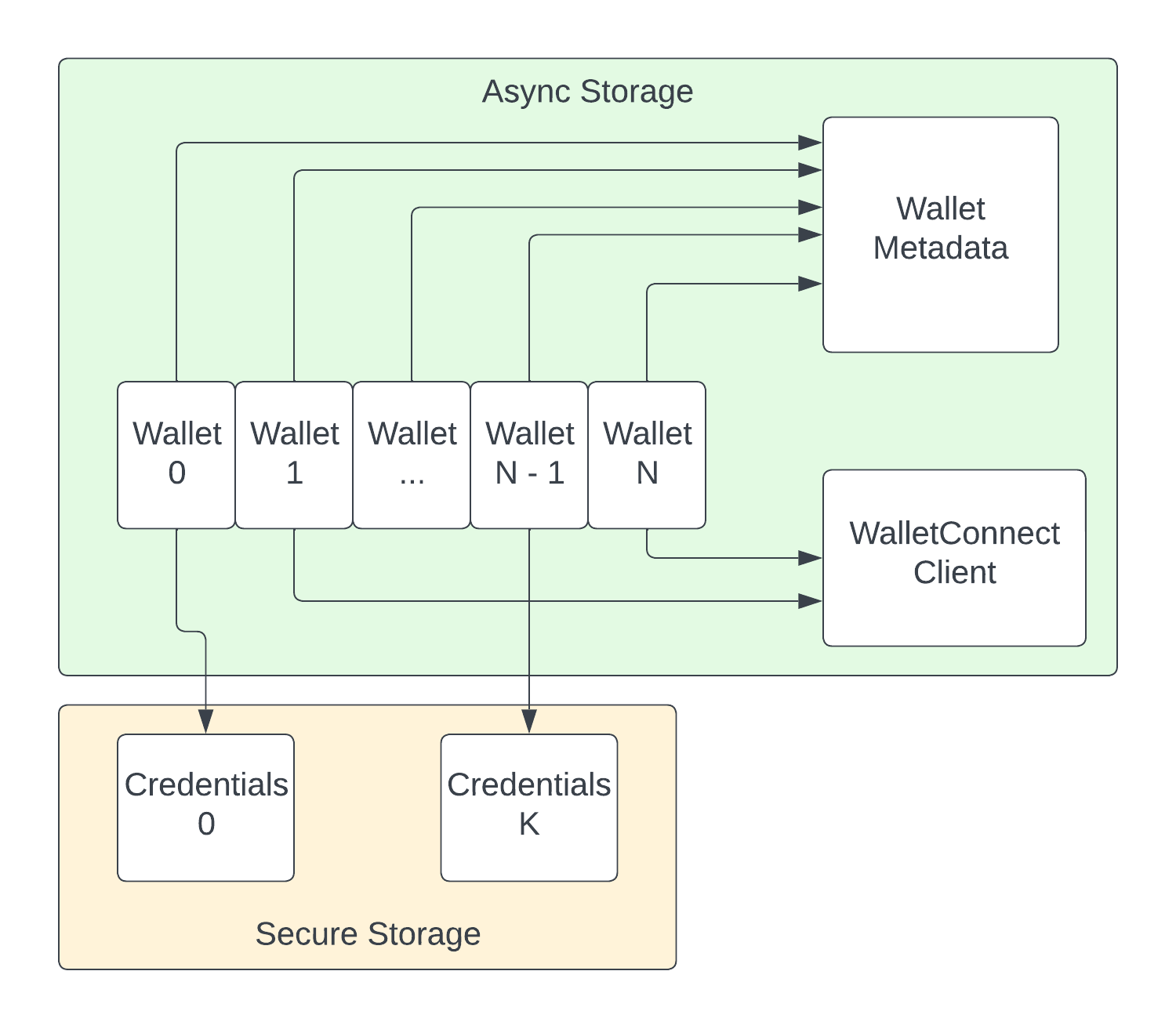
Here is a high-level diagram of how wallet info and credentials are managed by the SDK:
Terms
Wallet Metadata
Wallet Metadata includes all non-sensitive info about each specific wallet.
This includes a label for the type of wallet, such as local, wallet-connect, read-only, or any type declared on wallet creation.
Metadata optionally contains wallet name, default currency type, unique numeric identifier in the Node API, and a generic map to store any additional data.
In the SDK, the specific type for Wallet Metadata is WalletDetails, and it has the following shape:
type WalletType = "local" | "external" | "viewer" | string;
type WalletDetails = {
walletType: WalletType;
name?: string;
wid?: number;
address: string;
additionalInfo?: Record<string, unknown>;
defaultCurrency?: CurrencyType;
};
WalletConnect Client
In the diagram, the WalletConnect Client box is meant to represent any generic external signer provided to the SDK that does not reference wallet credentials held in secure storage.
Each wallet maintains a reference to its designated signer. The only requirement for a signer to be compatible with the Node SDK is that it must implement the Signer interface from ethersjs.
Credentials
The default wallet type in the Node SDK is the local wallet; one that has its credentials encrypted and stored in secure storage on device. Depending on how the wallet created, this object can contain mnemonic, derivaion path, and / or private key. If the wallet was freshly created using the SDK, then the credentials will include all three. If the wallet was created using credentials provided by the developer, then the object will contain whatever fields were provided. All credentials in secure storage also contain a field designating the version of credential storage that was used.
The credentials thus have the following shape:
type Credentials = {
privateKey: string;
mnemonic?: string;
derivationPath?: string;
_v: number;
};
Managing Multiple Wallets
The SDk exposes multiple hooks to interact with the wallet storage mechanism, the most important one being useAllWallets
useAllWallets
This hook returns an array of wallet details, the index of the currently active wallet, and a callback to set the index of the currently active wallet.
type UseAllWalletsReturnType = {
wallets: WalletDetails[];
activeWalletIndex: number;
setActiveWalletIndex: (n: number | ((current: number) => number)) => void;
};
WalletDetails has the same shape as described above for wallet metadata.
Here is an example of a screen that displays all wallets stored, and allows the user to switch to any other wallet.
const WalletManagementScreen = () => {
const {
wallets,
activeWalletIndex,
setActiveWalletIndex
} = useAllWallets()
return <View>
{
wallets.map(({name, address}, i) => (
<Pressable onPress={() => setActiveWalletIndex(i)} >
<RowBetween>
<Text>{name ?? shortenAddress(address)} </Text>
<Text>{i === activeWalletIndex ? "✅" : " "}
</RowBetween>
</Pressable>
))
}
</View>
}
Other Hooks
useWalletName
Returns the name of the currently active wallet, and a callback to change the name of the currently active wallet.
useWalletType
Returns the type of the currenlty active wallet, and a callback to change the type of the currently active wallet. Note that changing the type of the wallet if a wallet is already of type local will affect behavior when loading wallet signer.
useWalletAdditionalInfo
Returns the additionalInfo object from wallet details. This is where the developer can store any arbitrary information about the wallet. Merge a new object into the existing info object through the callback returned from this hook.